Prometheus Alertmanager 的源码导读
Alertmanager 是 Prometheus 提供的报警分发平台,它主要满足的是报警的路由、分组、抑制、去重等常见需求。
整体报警控制逻辑
Alertmanager 将报警路由组织成树状结构:
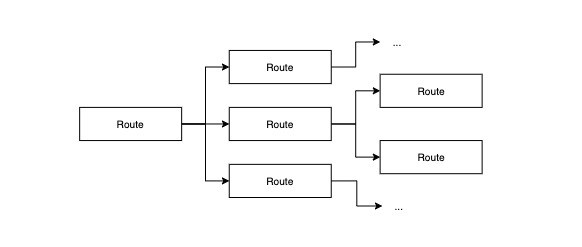
每条报警信息进入 Alertmanager 后,都会被流转给根路由,然后根据每个路由的配置决定是否递归地继续往下传播。每条报警信息最终都会匹配到一棵路由子树,如下图所示:
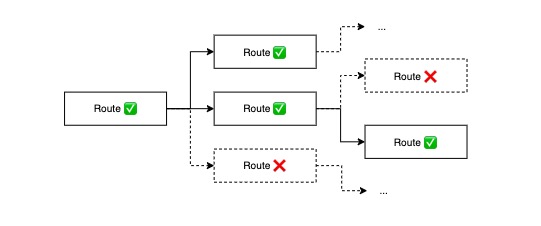
这棵子树上的路由就是可能发出报警信息的路由。那么报警信息在单个路由内部是如何处理的?
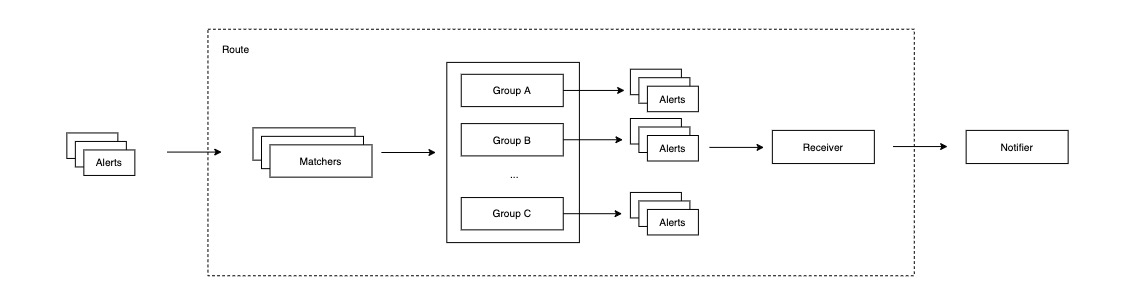
每个路由内部会有一组匹配器 (Matcher) 负责匹配报警信息,匹配成功则表示路由命中。进入路由内部后,会根据报警信息的一些特征将其分配到某个特定的组 (Group),每个组内拥有独立的通知 (Notify) 处理逻辑,如抑制、冷却、去重,最终满足一定条件后,路由会根据接收人 (Receiver) 配置,将报警信息通过通知媒介传递给相应的负责人。
项目架构
Alertmanager 项目内部大体可以分为 model、base、business、communication 四层,如下图所示:
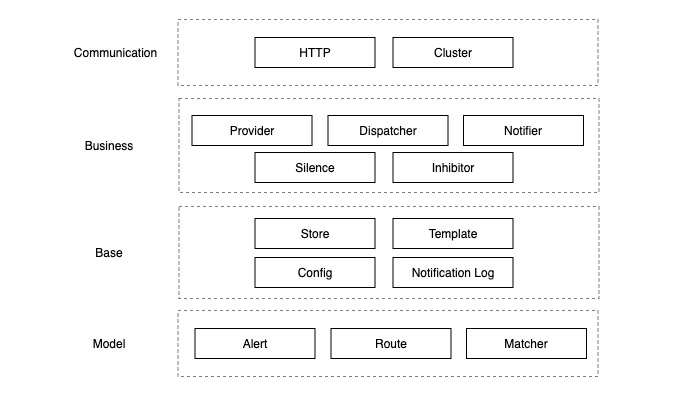
此分层非官方分层,实际源码结构并未按此分层来组织,且层与层之间的界限也不明显,这里仅供下文分析参考。
Model
model 层中定义了 Alertmanager 的主要数据模型,报警 (Alert)、路由 (Route) 以及匹配器 (Matcher)。
Alert
由于 Alert 是贯穿整个 Prometheus
生态的核心概念,因此它的定义实际上并不在 Alergmanager 项目中,而是在
github.com/prometheus/common 项目的 model
中,这里截取源码中的定义如下所示:
1 | // Alert is a generic representation of an alert in the Prometheus eco-system. |
Labels 是 Alert 的特征描述,它可以被用来区分不同的 Alert,也是后续路由、分组、通知的依据;Annotations 是 Alert 的一些附加信息,能够影响 Alert 在系统内部处理的逻辑,不会被用来标识 Alert 本身;StartsAt 和 EndsAt 标识报警的开始时间以及结束时间;GeneratorURL 用于追溯报警源头。
Route
路由树是 Alertmanager 的核心,信息分发的主体,其结构体具体如下:
1 | // A Route is a node that contains definitions of how to handle alerts. |
Route 是树状结构,parent 和 Routes 就是每个节点的父节点和子节点;Matchers 用于匹配 Alerts;Continue 决定是否继续尝试在其它兄弟节点匹配。RouteOpts 结构如下:
1 | // RouteOpts holds various routing options necessary for processing alerts |
Receiver 是通知对象的标识信息,它可以对应着最终的通知媒介,比如一组邮箱、一个 Slack channel 或是通用的 webhook;GroupBy 是路由分组的属性集合,如果这个集合有 cluster 和 business 两个属性,那么所有来自于同一集群,同属一个业务线的报警信息就会被分发到这个集合中;当 Route 节点收到报警信息后,会等待 GroupWait 长度的时间,合并相同的报警信息,批量发送;如果某 Group 中迎来了新的报警 (和已知的报警在 Labels 上有所不同),那么经过 GroupInterval 后,新的消息就会被发出;如果该 Group 没有迎来新的报警,且老的报警仍然处于活跃状态,那么经过 RepeatInterval 后,老的报警消息会继续被发送。通常 RepeatInterval 要比 GroupInterval 大许多。
Matcher
Matcher 用于匹配报警信息,可以被用在多个地方,如:
- Route:用于决定报警信息是否被捕获
- Silence/Inhibitor:用于决定报警信息是否被抑制
- …
其结构十分简单:
1 | // Matcher defines a matching rule for the value of a given label. |
单个 Matcher 匹配一个 Label,分成完全匹配和正则匹配两种模式。
Base
Base 层是 Alertmanager 内部所需的基础逻辑模块,包括 Store、Template、Config 以及 Notification Log。Template 封装了 go 原生的 html template 和 text template,主要用于格式化报警通知的具体内容;Config 负责定义、加载 Alertmanager 的配置信息,详细配置可参考官方文档。下面详细介绍 Store 和 Notification Log。
Store
Store 是内存中的一组 Alerts 集合,它支持往集合中添加、删除、获取 Alert,同时支持异步的对已经解决的 Alert 做垃圾收集,其所有操作都满足线程安全。Store 在 3 个地方被使用:
Aggregation Group:作为单个 Route 中每个 Group 的 Alerts 容器
Mem Provider:作为单个 Alertmanager 实例内部存放全量 Alerts 的容器
Inhibitor:作为每条 Inhibitor Rule 中缓存的 Source Alerts 缓存容器
Notification Log
Notification Log,简称 NFLog,用于记录同一集群内所有 Alertmanager 实例曾经触发的通知日志。通过本实例发出的通知消息在被 NFLog 记录的同时,会通过 gossip 的方式广播到其它实例,其它实例获得该信息后就能对通知去重,避免重复向相关人员发送通知。此外,与 Store 类似,NFLog 会定期地将过期通知消息垃圾收集,也会定期将当前所有日志快照写出到本地日志文件。NFLog 利用 CRDT (context-free replicated data type) 在不同实例之间同步数据,保证最终一致性,是 Alertmanager 高可用架构的重要组件。
Business
Provider
Provider 向 Alertmanager 提供 Alerts 信息的中心存储。Alertmanager 将客户端发送来的 Alert 信息放入 Provider 中,后者向 Alertmanager 的其它组件提供订阅消息,其核心接口如下所示:
1 | // Alerts gives access to a set of alerts. All methods are goroutine-safe. |
Provider 仅仅是定义了接口,但这个中心存储可以有多种实现,Alertmanager
默认提供了内存版本的实现,即
provider/mem/mem.go,如果其它团队想要二次开发,也可以基于此提供持久化存储版本的实现。
Dispatcher
Dispatcher 负责串联 Alertmanager 的核心报警控制逻辑,是 Alertmanager 的指挥中枢。其处理流程如下图所示:
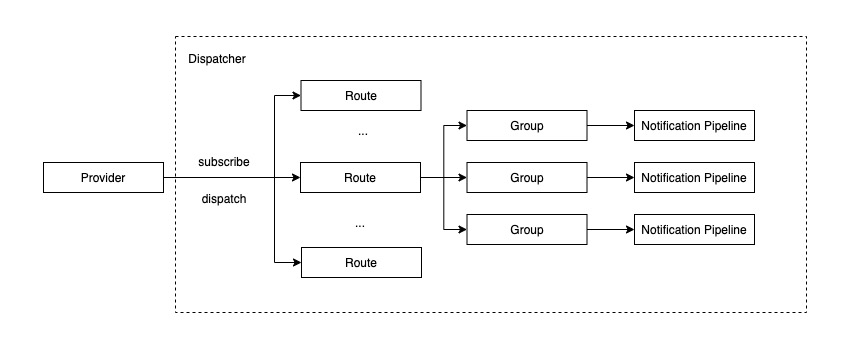
Dispatcher 初始化时,会通过异步线程从 Provider 订阅的 Alerts 信息。每当新的 Alert 信息出现,然后将其转发给路由树,后者递归地为 Alert 寻找匹配的路由节点 (Route),找到符合条件的一组路由节点后,将 Alert 放入每个节点对应的 Group 中,同时异步地执行对应的通知流水线 (Notification Pipeline)。
Notifier
Notifier 负责消息的去重、抑制、发送、同步,整个过程被组织成一条流水线 (Pipeline),后者进而由若干个可配置的 (Stage) 构成:
1 | // A Stage processes alerts under the constraints of the given context. |
每个 Stage 结束时会返回允许进入下一个 Stage 的 Alerts 列表,如果后者是一个空列表,流水线就会提前结束。在当前版本 (Alertmanager v0.2.1) 中的一条通知流水线是如何构成的?
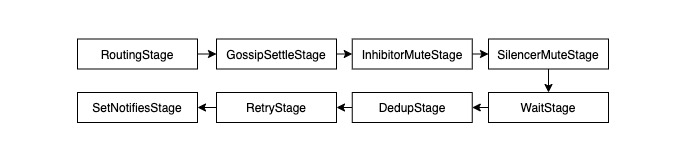
- RoutingStage:关联同一条报警信息的各接收方与其对应的 MultiStage
- GossipSettleStage:等待一个足够长的时间,尽量保证多个实例之间的信息同步完毕
- InhibitorMuteStage/SilencerMuteStage:确定是否应该抑制,需要抑制的 Alert 会被过滤
- WaitStage:等待一个足够长的时间,不同实例等待的时间不同,从而尽可能保证去重逻辑生效
- DedupStage:通过 NFLog 执行去重逻辑
- RetryStage:发送消息,若失败则重试
- SetNotifiesStage:将发送记录写进 NFLog 中
此外,还有两个流程控制 Stage:
- MultiStage:将多个 Stage 串行执行
- FanoutStage:将多个 Stage 并发执行
Silence & Inhibitor
Silence 与 Inhibitor 分别实现两种报警抑制方式。Silence 允许用户指定时间范围以及匹配器列表来抑制特定的报警;Inhibitor 允许用户关联不同的报警信息,当出现 A 类报警时,抑制 B 类报警。
Communication
通信层负责处理 Alertmanager 实例与客户端以及集群内其它实例的沟通逻辑。
HTTP
Alertmanager 曾经有过两个版本的 HTTP 层实现,v2 版本使用 openapi 规范定义交互协议,并利用相应的工具 (swagger) 生成 server stub 和 client stub,再基于此实现相应的业务逻辑,这层逻辑比较薄,内容不多,这里不再赘述。
Cluster
Cluster 是 Alertmanager 的高可用模块,主要负责集群元信息的维护,如集群内部有哪些实例,每个实例的健康状况如何,有新的实例加入或者故障实例移除时,需要做哪些相应的更新。在启动时,实例需要通过一个或多个已知的实例来传递自己加入集群的消息,通过实例间的 gossip,使得集群中所有实例中维护的集群元信息保持最终一致。
设计思考
以下讨论我个人对 Alertmanager 的一些设计决定的分析:
通过 CRDT 和 memberlist 实现 AP 系统
如果我们的各个微服务已经做到了高可用,监控本身也需要高可用。通常的做法就是让两个 Prometheus 实例去采集相同的数据,如下图所示:
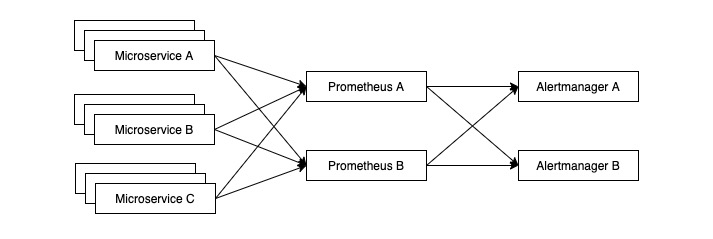
自然而然地,我们也不能让 Alertmanager 出现单点故障,因此就需要建立 Alertmanager Cluster 达到高可用。需要注意的是,报警是个 AP 系统,可用性是第一位,如果报警系统不可用,就会出现故障发生但无人知晓的情况。对于报警系统来说,C (consistency) 并不需要得到绝对保证,同样出现不一致,多报要比漏报更能够被接受。基于以上考虑,Alertmanager 通过 memberlist 的 gossip 机制实现 Alertmanager 的集群管理,多个 Prometheus 会将报警信息打到所有实例上,再通过不同实例间的交流和报警去重逻辑来最大程度上避免重复报警。如果实例间出现网络分区,可能出现多次报警的情况。除此之外,不同 Alertmanager 之间存在需要共享的数据,如通知记录 (Notification Log) 和抑制规则,Alertmanager 通过 CRDT 来解决数据冲突,保证数据的最终一致性。
以内存作为主要存储
报警信息有两个主要特点:时效性强和数据量小。前者体现在报警通知在发出之后,已经不存在在线处理、分析的价值;后者体现在报警过多,相应的开发团队会及时处理,遏制报警数量的增长。基于这些特点,选择内存作为即时报警数据的存储,定时做垃圾清理足以应对日常需求,即便未来有离线分析的需求,在 Provider 层面增加持久化存储的实现支持即可。
基于树状结构的分发逻辑和配置继承、定制化
公司的组织架构是树状结构,根据康威定律,研发团队及微服务分层分组也会收敛到树状结构。报警的目标之一是将问题快速反馈给相关的人或者团队,那么通过树状结构组织分发逻辑是顺势而为。此外,树状结构可以方便地实现配置的继承,而在单个节点上覆盖配置又能方便地支持定制化。
通过报警信息是否持续出现判断问题解决与否
如何判断报警反映的问题解决与否,是报警平台必须要面对的问题。有两种基本思路:
- 手动:服务维护者修复问题后手动标记
- 自动:报警平台根据报警信息的出现规律利用规则自动判断
从准确性角度分析,手动标记的准确度取决于服务维护者的判断能力,绝大多数情况下能准确反馈情况,而自动标记存在误判可能;从用户体验上看,手动标记会给服务维护者带来额外的操作负担,也可能出现漏标、多标、误标的情况,而自动标记则无需服务维护者参与。
Alertmanager 采用的是自动方案,在报警信息第一次出现时,直接标记其结束时间为 5 分钟后 (全局的 resolve_timeout 配置决定),若在 5 分钟内报警未再次出现,则认为报警处于已经解决的状态;若在 5 分钟内报警再次出现,则将报警的结束时间延长 5 分钟。
小结
Alertmanager 是对中、大型研发团队中报警分发逻辑的一次抽象尝试,从模型设计、分发逻辑、通知流水线到典型的 AP 系统高可用方案,都值得我们学习和讨论。